Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
PROXY SOLUTIONS
Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
Reliable mobile data extraction, powered by real 4G/5G mobile IPs.
Guaranteed bandwidth — for reliable, large-scale data transfer.
For time-sensitive tasks, utilize residential IPs with unlimited bandwidth.
Fast and cost-efficient IPs optimized for large-scale scraping.
A powerful web data infrastructure built to power AI models, applications, and agents.
High-speed, low-latency proxies for uninterrupted video data scraping.
Extract video and metadata at scale, seamlessly integrate with cloud platforms and OSS.
6B original videos from 700M unique channels - built for LLM and multimodal model training.
Get accurate and in real-time results sourced from Google, Bing, and more.
Execute scripts in stealth browsers with full rendering and automation
No blocks, no CAPTCHAs—unlock websites seamlessly at scale.
Get instant access to ready-to-use datasets from popular domains.
PROXY PRICING
Full details on all features, parameters, and integrations, with code samples in every major language.
LEARNING HUB
ALL LOCATIONS Proxy Locations
TOOLS
RESELLER
Get up to 50%
Contact sales:partner@thordata.com
Proxies $/GB
Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
Reliable mobile data extraction, powered by real 4G/5G mobile IPs.
For time-sensitive tasks, utilize residential IPs with unlimited bandwidth.
Fast and cost-efficient IPs optimized for large-scale scraping.
Guaranteed bandwidth — for reliable, large-scale data transfer.
Scrapers $/GB
Fetch real-time data from 100+ websites,No development or maintenance required.
Get real-time results from search engines. Only pay for successful responses.
Execute scripts in stealth browsers with full rendering and automation.
Bid farewell to CAPTCHAs and anti-scraping, scrape public sites effortlessly.
Dataset Marketplace Pre-collected data from 100+ domains.
Data for AI $/GB
A powerful web data infrastructure built to power AI models, applications, and agents.
High-speed, low-latency proxies for uninterrupted video data scraping.
Extract video and metadata at scale, seamlessly integrate with cloud platforms and OSS.
6B original videos from 700M unique channels - built for LLM and multimodal model training.
Pricing $0/GB
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Docs $/GB
Full details on all features, parameters, and integrations, with code samples in every major language.
Resource $/GB
EN
代理 $/GB
数据采集 $/GB
AI数据 $/GB
定价 $0/GB
产品文档
资源 $/GB
简体中文$/GB


As e-commerce continues to dominate retail in 2026, platforms like Amazon host millions of customer reviews that offer invaluable insights into product performance, consumer preferences, and market trends. Web scraping Amazon reviews with Python enables businesses, researchers, and developers to automate data collection, transforming raw feedback into actionable insights. This guide provides a comprehensive, step-by-step approach to building a robust Amazon review scraper.
Whether you’re new to web scraping reviews in Python or looking to optimize your existing tools, this article covers everything from setup to advanced integrations.
Web scraping reviews with Python isn’t just a technical exercise—it’s a strategic tool for gaining a competitive edge. In 2026, with AI-driven analytics on the rise, scraping Amazon reviews helps companies monitor sentiment, identify pain points, and benchmark against competitors.
● Sentiment Analysis: Aggregate ratings and text to gauge overall customer satisfaction.
● Trend Detection: Spot emerging patterns in feedback over time.
● Product Improvement: Use detailed reviews to refine offerings and boost sales.
● Market Research: Compare reviews across products without manual effort.
By leveraging Python for web scraping reviews, you can process thousands of entries efficiently. However, for large-scale operations, Thordata’s SERP Scraper API shines by providing seamless access to data without the hassle of blocks or bans.
Before diving into code, prepare your environment to ensure smooth web scraping of Amazon reviews with Python. This setup minimizes errors and supports efficient data handling.
You’ll need Python 3.8 or higher. Install the following packages via pip:
text
pip install requests beautifulsoup4 pandas lxml
● Requests: For sending HTTP requests to Amazon pages.
● BeautifulSoup: To parse HTML and extract review elements.
● Pandas: For structuring scraped data into DataFrames and exporting to CSV.
● lxml: A fast parser for BeautifulSoup.
These libraries form the core of most Python web scraping projects. If you're facing installation issues, refer to Python's official documentation.
To avoid detection, use custom headers mimicking a real browser. For added reliability, integrate residential proxies early— they offer rotating residential IPs that boost success rates to over 99%, far superior to free options.
Amazon's product pages (e.g., https://www.amazon.com/dp/B098FKXT8L) display a limited set of local and global reviews. As of 2026, reviews are typically wrapped in <div data-hook="review"> elements under IDs like #cm-cr-dp-review-list for local reviews and #cm-cr-global-review-list for global ones.
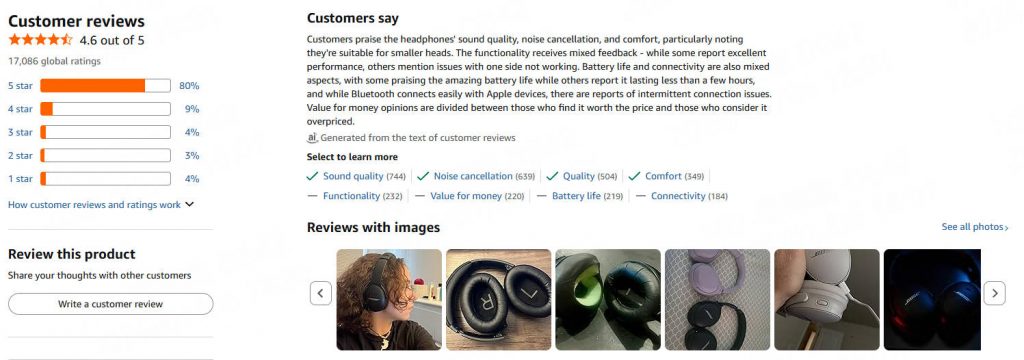
● Author: .a-profile-name
● Rating: .review-rating > span
● Date: .review-date
● Title and Content: Vary by local/global, often under .review-title and .review-text
● Images: .review-image-tile or similar
● Verified: span.a-size-mini
Inspect the page using browser dev tools to confirm selectors as the structure evolves. For full reviews, consider extending to /product-reviews/ASIN with pagination.
|
Element |
CSS Selector |
Description |
|
Author |
.a-profile-name |
Reviewer's name |
|
Rating |
.review-rating > span |
Star rating (e.g., "5.0") |
|
Date |
.review-date |
Review timestamp |
|
Title (Local) |
.review-title span:not([class]) |
Review headline |
|
Content (Local) |
.review-text |
Full review body |
|
Images |
.review-image-tile |
Attached photos |
This table summarizes core selectors for quick reference in your web scraping reviews Python project.
Let's build the scraper incrementally.
Start by importing libraries and defining the ASIN (Amazon Standard Identification Number).
Python
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import pandas as pd
asin = "B098FKXT8L"
custom_headers = {
"Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8",
"Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.9",
"Connection": "keep-alive",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/135.0"
}
def get_soup(url):
response = requests.get(url, headers=custom_headers)
if response.status_code != 200:
print("Error in getting webpage")
return None
return BeautifulSoup(response.text, "lxml")
This function fetches and parses the page.
Define a function to extract details from each review element.
Python
def extract_review(review, is_local=True):
author_element = review.select_one(".a-profile-name")
author = author_element.text.strip() if author_element else "Unknown"
rating_element = review.select_one(".review-rating > span")
rating = rating_element.text.replace("out of 5 stars", "").strip() if rating_element else "0"
date_element = review.select_one(".review-date")
date = date_element.text.strip() if date_element else "Unknown"
if is_local:
title = review.select_one(".review-title span:not([class])").text.strip() if review.select_one(".review-title span:not([class])") else ""
content = ' '.join(review.select_one(".review-text").stripped_strings) if review.select_one(".review-text") else ""
img_selector = ".review-image-tile"
else:
title = review.select_one(".review-title .cr-original-review-content").text.strip() if review.select_one(".review-title .cr-original-review-content") else ""
content = ' '.join(review.select_one(".review-text .cr-original-review-content").stripped_strings) if review.select_one(".review-text .cr-original-review-content") else ""
img_selector = ".linkless-review-image-tile"
verified_element = review.select_one("span.a-size-mini")
verified = verified_element.text.strip() if verified_element else None
image_elements = review.select(img_selector)
images = [img.attrs.get("data-src") for img in image_elements if img.attrs.get("data-src")] if image_elements else None
return {
"type": "local" if is_local else "global",
"author": author,
"rating": rating,
"title": title,
"content": content.replace("Read more", ""),
"date": date,
"verified": verified,
"images": images
}
This handles variations between local and global reviews.
Collect reviews with this function:
Python
def get_reviews(soup):
reviews = []
local_reviews = soup.select("#cm-cr-dp-review-list > div[data-hook='review']")
global_reviews = soup.select("#cm-cr-global-review-list > div[data-hook='review']")
for review in local_reviews:
reviews.append(extract_review(review, is_local=True))
for review in global_reviews:
reviews.append(extract_review(review, is_local=False))
return reviews
Exporting Scraped Data to CSV
Wrap it up in main:
Python
def main():
search_url = f"https://www.amazon.com/dp/{asin}"
soup = get_soup(search_url)
if soup is None:
return
reviews = get_reviews(soup)
df = pd.DataFrame(reviews)
df.to_csv(f"reviews_{asin}.csv", index=False)
print("Data exported to CSV.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Run this script to save reviews in a CSV file.
Here's the complete, runnable script combining all parts:
Python
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import pandas as pd
asin = "B098FKXT8L"
custom_headers = {
"Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8",
"Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.9",
"Connection": "keep-alive",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/135.0"
}
def get_soup(url):
response = requests.get(url, headers=custom_headers)
if response.status_code != 200:
print("Error in getting webpage")
return None
return BeautifulSoup(response.text, "lxml")
def extract_review(review, is_local=True):
author_element = review.select_one(".a-profile-name")
author = author_element.text.strip() if author_element else "Unknown"
rating_element = review.select_one(".review-rating > span")
rating = rating_element.text.replace("out of 5 stars", "").strip() if rating_element else "0"
date_element = review.select_one(".review-date")
date = date_element.text.strip() if date_element else "Unknown"
if is_local:
title = review.select_one(".review-title span:not([class])").text.strip() if review.select_one(".review-title span:not([class])") else ""
content = ' '.join(review.select_one(".review-text").stripped_strings) if review.select_one(".review-text") else ""
img_selector = ".review-image-tile"
else:
title = review.select_one(".review-title .cr-original-review-content").text.strip() if review.select_one(".review-title .cr-original-review-content") else ""
content = ' '.join(review.select_one(".review-text .cr-original-review-content").stripped_strings) if review.select_one(".review-text .cr-original-review-content") else ""
img_selector = ".linkless-review-image-tile"
verified_element = review.select_one("span.a-size-mini")
verified = verified_element.text.strip() if verified_element else None
image_elements = review.select(img_selector)
images = [img.attrs.get("data-src") for img in image_elements if img.attrs.get("data-src")] if image_elements else None
return {
"type": "local" if is_local else "global",
"author": author,
"rating": rating,
"title": title,
"content": content.replace("Read more", ""),
"date": date,
"verified": verified,
"images": images
}
def get_reviews(soup):
reviews = []
local_reviews = soup.select("#cm-cr-dp-review-list > div[data-hook='review']")
global_reviews = soup.select("#cm-cr-global-review-list > div[data-hook='review']")
for review in local_reviews:
reviews.append(extract_review(review, is_local=True))
for review in global_reviews:
reviews.append(extract_review(review, is_local=False))
return reviews
def main():
search_url = f"https://www.amazon.com/dp/{asin}"
soup = get_soup(search_url)
if soup is None:
return
reviews = get_reviews(soup)
df = pd.DataFrame(reviews)
df.to_csv(f"reviews_{asin}.csv", index=False)
print("Data exported to CSV.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
This code is optimized for 2026 Amazon structures, with error handling for robustness.
While custom Python scripts offer flexibility, scaling web scraping reviews can be challenging. Thordata's Amazon Scraper API addresses this by providing enterprise-grade solutions.
For smaller projects, Thordata offers a free trail to get started. They ensure connection stability and basic anti-scraping bypass. For larger scales, Thordata Residential Proxies mimic real user behavior, minimizing blocks—ideal for web scraping Amazon reviews with Python.
To maintain a positive user experience and comply with standards:
1. Rate-limit requests to avoid overloading servers.
2. Use ethical data practices—don't misuse personal info.
3. Check Amazon's robots.txt and terms; scraping public data is common but consult legal advice.
4. Monitor for changes in page structure.
5. Opt for Thordata to ensure compliant, efficient scraping.
Web scraping Amazon reviews with Python empowers data-driven decisions in 2026's competitive landscape. By following this guide and leveraging Thordata's superior scraping products, you can achieve reliable, scalable results with minimal effort. Start small with the provided code, then scale up with Thordata for professional-grade performance.
Contact us at support@thordata.com for tailored advice.
Frequently asked questions
How to Scrape All Amazon Reviews with Python?
To scrape beyond the initial page, add pagination by looping through URLs like https://www.amazon.com/product-reviews/{asin}?pageNumber={page}. Use a while loop until no more reviews are found, and integrate Thordata proxies to handle volume without blocks.
What Are the Best Python Libraries for Web Scraping Amazon Reviews?
Top libraries include Requests for HTTP, BeautifulSoup for parsing, Pandas for data export, and Selenium for dynamic content. For advanced needs, combine with Thordata's API to simplify integration.
How to Avoid Blocks When Web Scraping Amazon Reviews with Python?
Yes, for public data if you respect robots.txt and ToS—focus on ethical crawling and scraping to avoid blocks, prioritizing proxies and rate limits.
About the author

Jenny is a Content Specialist with a deep passion for digital technology and its impact on business growth. She has an eye for detail and a knack for creatively crafting insightful, results-focused content that educates and inspires. Her expertise lies in helping businesses and individuals navigate the ever-changing digital landscape.
The thordata Blog offers all its content in its original form and solely for informational intent. We do not offer any guarantees regarding the information found on the thordata Blog or any external sites that it may direct you to. It is essential that you seek legal counsel and thoroughly examine the specific terms of service of any website before engaging in any scraping endeavors, or obtain a scraping permit if required.
 Looking for
Top-Tier Residential Proxies?
Looking for
Top-Tier Residential Proxies? 您在寻找顶级高质量的住宅代理吗?
您在寻找顶级高质量的住宅代理吗?
5 Best Etsy Scraper Tools in 2026
This article evaluates the top ...
Yulia Taylor
2026-02-09

What is a Headless Browser? Top 5 Popular Tools
A headless browser is a browse ...
Yulia Taylor
2026-02-07

Best Anti-Detection Browser in 2026
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2026-02-08 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-06
What Is a UDP Proxy? Use Cases and Limits
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-02-06 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-06

Geographic Pricing Explained: Why Prices Change by Location
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-02-05 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-05

How to Use Proxies in Python: A Practical Guide
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-02-05 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-05
What Is an Open Proxy? Risks of Free Open Proxies
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-02-04 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-04

What Is a PIP Proxy? How It Works, Types, and Configuration?
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2025-02-04 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-04
TCP and UDP: What’s Different and How to Choose
Xyla Huxley Last updated on 2026-02-04 10 min read […]
Unknown
2026-02-04