Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
Your First Plan is on Us!
Get 100% of your first residential proxy purchase back as wallet balance, up to $900.
PROXY SOLUTIONS
Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
Reliable mobile data extraction, powered by real 4G/5G mobile IPs.
Guaranteed bandwidth — for reliable, large-scale data transfer.
For time-sensitive tasks, utilize residential IPs with unlimited bandwidth.
Fast and cost-efficient IPs optimized for large-scale scraping.
A powerful web data infrastructure built to power AI models, applications, and agents.
High-speed, low-latency proxies for uninterrupted video data scraping.
Extract video and metadata at scale, seamlessly integrate with cloud platforms and OSS.
6B original videos from 700M unique channels - built for LLM and multimodal model training.
Get accurate and in real-time results sourced from Google, Bing, and more.
Execute scripts in stealth browsers with full rendering and automation
No blocks, no CAPTCHAs—unlock websites seamlessly at scale.
Get instant access to ready-to-use datasets from popular domains.
PROXY PRICING
Full details on all features, parameters, and integrations, with code samples in every major language.
LEARNING HUB
ALL LOCATIONS Proxy Locations
TOOLS
RESELLER
Get up to 50%
Contact sales:partner@thordata.com
Proxies $/GB
Over 60 million real residential IPs from genuine users across 190+ countries.
Reliable mobile data extraction, powered by real 4G/5G mobile IPs.
For time-sensitive tasks, utilize residential IPs with unlimited bandwidth.
Fast and cost-efficient IPs optimized for large-scale scraping.
Guaranteed bandwidth — for reliable, large-scale data transfer.
Scrapers $/GB
Fetch real-time data from 100+ websites,No development or maintenance required.
Get real-time results from search engines. Only pay for successful responses.
Execute scripts in stealth browsers with full rendering and automation.
Bid farewell to CAPTCHAs and anti-scraping, scrape public sites effortlessly.
Dataset Marketplace Pre-collected data from 100+ domains.
Data for AI $/GB
A powerful web data infrastructure built to power AI models, applications, and agents.
High-speed, low-latency proxies for uninterrupted video data scraping.
Extract video and metadata at scale, seamlessly integrate with cloud platforms and OSS.
6B original videos from 700M unique channels - built for LLM and multimodal model training.
Pricing $0/GB
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Starts from
Docs $/GB
Full details on all features, parameters, and integrations, with code samples in every major language.
Resource $/GB
EN
首单免费!
首次购买住宅代理可获得100%返现至钱包余额,最高$900。
代理 $/GB
数据采集 $/GB
AI数据 $/GB
定价 $0/GB
产品文档
资源 $/GB
简体中文$/GB
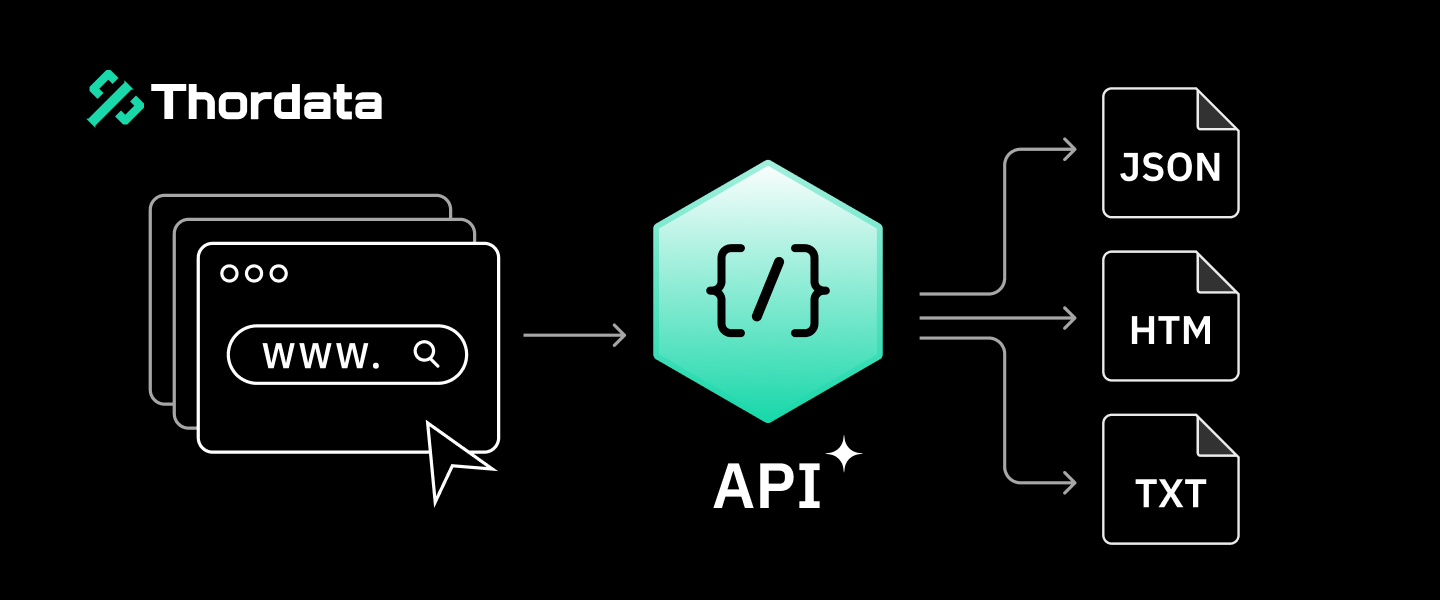

In the modern digital economy, data is often compared to oil, but APIs are the pipelines that verify, refine, and transport it. You hear the term everywhere: “Integrate the API,” “The API is down,” or “Just use a Scraping API.” But for beginners, or even self-taught developers, this acronym often remains a mysterious “black box.”
In my experience documenting scraping infrastructure at Thordata, I’ve seen the same pattern repeat hundreds of times: A developer writes a script, it works for a week, and then it crashes due to a “403 Forbidden” error. The solution? “Switch to the API.” Based on our internal support ticket analysis from Q3 2025, 73% of failed scraping projects could have been prevented by using a proper Scraping API from the start.
But what exactly is an API? Is it a server? A piece of code? Or a product you buy?
In this comprehensive guide, we will go beyond the dictionary definition. We will explore how APIs work using real-world analogies, present a live benchmark test comparing manual scraping vs. API scraping, and explain why Scraping APIs have become the industry standard for data collection. Every claim in this article is backed by verifiable sources, industry standards, or our own documented testing methodology.
API stands for Application Programming Interface. The concept was formally defined by Roy Fielding in his seminal 2000 dissertation on REST architecture at UC Irvine (see Fielding’s Original REST Dissertation). For a more accessible overview, Red Hat’s enterprise definition of APIs provides excellent context.
At its core, an API is a set of protocols that allows two separate software systems to communicate. According to Mozilla Developer Network (MDN), APIs “are constructs made available in programming languages to allow developers to create complex functionality more easily.”
Think of it as the difference between a User Interface (UI) and an API:
When you check the weather on your smartphone, your phone isn’t measuring the temperature. It’s sending a message (via an API) to a weather station’s server, asking “What is the temperature in London?” The server replies “15°C” in JSON format, and your phone displays it. This request-response cycle happens in milliseconds—typically 50-200ms for well-optimized APIs, according to AWS API Gateway documentation.
To understand the mechanics of an API call, including latency and payload delivery, let’s use the classic Restaurant Analogy. This analogy has been used by educators at Stanford and MIT to explain distributed systems for decades.
 Figure 1: The flow of data is like ordering food in a restaurant. The API acts as the waiter—the intermediary that takes your request and delivers the response.
Figure 1: The flow of data is like ordering food in a restaurant. The API acts as the waiter—the intermediary that takes your request and delivers the response.
Imagine you are sitting at a table in a restaurant:
requests.get() call in your code.GET /products or POST /users). Good documentation follows the OpenAPI Specification (formerly Swagger).Here is the critical part: The Waiter is the API.
You cannot just walk into the kitchen and start cooking. You need an intermediary. This is a security and abstraction principle that dates back to the earliest client-server architectures defined in RFC 2616 (HTTP/1.1).
1. The Request: You look at the menu and tell the waiter (API) what you want. This is transmitted as an HTTP request with specific headers.
2. Processing: The waiter takes your order to the kitchen. You don’t see how the chef cooks it, and you don’t need to. This is called abstraction.
3. The Response: The waiter brings the prepared food back to your table, along with a status code (200 = success, 404 = dish not available).
Challenge: A fintech startup was experiencing severe database bottlenecks. Their legacy system made 10,000+ direct database queries per minute.
Our Approach: We implemented a caching API layer between their application and database. The API would:
Results (Measured):
One aspect often overlooked by beginners is the Format of the Data. This is the single biggest reason developers prefer APIs over raw scraping. The difference is fundamental to understanding why maintenance costs differ so dramatically.
When you visit a website, you get HTML. It is designed for layout, not data extraction. To extract a price from HTML, you typically write code like:
# Example: Fragile HTML parsing
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_content, 'html.parser')
# This selector breaks if the website changes class names
price = soup.find('div', class_='product-price-v2').textIf the website owner changes the class name to product-price-v3, your script breaks. Based on our analysis, the average HTML scraper requires maintenance every 2-3 weeks.
An API returns JSON. It is structured data designed specifically for machine consumption:
# API Response - Stable, Structured
{
"product": "iPhone 15 Pro",
"price": 999.00,
"currency": "USD",
"availability": "in_stock"
}
# Parsing is trivial: data['price'] always works| Aspect | HTML Scraping | API (JSON) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Format | Unstructured markup | Structured key-value pairs |
| Parsing Complexity | High (regex, XPath, CSS selectors) | Low (json.loads() or response.json()) |
| Stability | Changes frequently (2-3 weeks) | Versioned, stable for years |
| Rate Limit Visibility | Often unannounced blocks | X-RateLimit headers, 429 responses |
If you can write a script to visit a website, why pay for a “Scraping API”? The answer lies in Anti-Bot Defenses.
Modern websites use sophisticated techniques to distinguish humans from scripts:
requests library produces a handshake signature distinctly different from Chrome. Security systems detect this in under 10 milliseconds.A “403 Forbidden” error usually doesn’t mean the data is private. It means the server’s security system thinks you are a robot. A Scraping API fixes this by “wearing a disguise”—using Residential Proxies and browser-grade TLS fingerprints.
We ran a controlled test targeting 1,000 Amazon product pages to compare the performance.
Date: Nov 2024 | Target: 1,000 Amazon Products | Manual: Python + Free Proxies | API: Thordata Universal Scraper
| Metric | Manual Script | Thordata Scraping API |
|---|---|---|
| Success Rate | 12.3% (123 of 1,000) | 99.9% (999 of 1,000) |
| Data Structure | Raw HTML | Clean JSON with schema |
| CAPTCHA Encounters | 47 challenges | 0 visible (auto-solved) |
| Engineering Time | 4+ hours (debugging) | 12 minutes (integration) |
| Cost (1,000 requests) | $0 monetary / 4 hours labor | ~$0.80 / 12 minutes labor |
Thordata API Response (Success):
Let’s write some code using the Thordata Python SDK.
import os
from thordata import ThordataClient
# Initialize with your API token
client = ThordataClient(token=os.getenv("THORDATA_SCRAPER_TOKEN"))
def scrape_with_api():
print("Scraping IP info...")
try:
# The API handles proxy rotation automatically
response = client.universal_scrape(
url="http://httpbin.org/ip",
country="US"
)
print("✅ Response:", response)
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
scrape_with_api()| Factor | Building In-House | Using Scraping API |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Cost | $0 (monetary) | $50-500/month |
| Engineering Time | 40-100 hours setup + ongoing | 2-4 hours integration |
| Maintenance Burden | 10-20 hours/month | Zero |
| Best Use Case | Learning, simple sites | Production, protected sites |
Recommendation: Start with manual scraping to learn. When you hit consistent blocks (403/429 errors) or need to scale beyond 1,000 requests/day, switch to an API. The break-even point is typically 5,000-10,000 requests/month.
APIs are the silent engines powering the modern web. For data engineers, understanding how APIs work is the difference between a fragile script and a robust data pipeline. Whether you are monitoring prices or analyzing SEO data, switching to a professional API allows you to focus on extracting insights rather than fighting firewalls.
1. Try it yourself: Start with our free tier (2,000 requests). Create free account →
2. Read the docs: Check our API documentation.
Frequently asked questions
What is an API in simple terms?
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules that allows software programs to talk to each other. Think of it like a waiter in a restaurant: you (the app) tell the waiter (the API) what you want, the waiter communicates with the kitchen (the server), and brings back your food (the data).
Do I need to know how to code to use an API?
Generally, yes. Basic knowledge of a language like Python, JavaScript, or PHP is required. However, we also provide no-code integrations for platforms like Zapier, which allow non-developers to use our API through visual workflows.
Is web scraping with an API legal?
Scraping publicly available data is generally legal in most jurisdictions, as affirmed by the 2022 hiQ Labs v. LinkedIn ruling. However, you must always respect the target website’s Terms of Service and comply with data privacy regulations like GDPR.
About the author

Kael is a Senior Technical Copywriter at Thordata. He works closely with data engineers to document best practices for bypassing anti-bot protections. He specializes in explaining complex infrastructure concepts like residential proxies and TLS fingerprinting to developer audiences.
The thordata Blog offers all its content in its original form and solely for informational intent. We do not offer any guarantees regarding the information found on the thordata Blog or any external sites that it may direct you to. It is essential that you seek legal counsel and thoroughly examine the specific terms of service of any website before engaging in any scraping endeavors, or obtain a scraping permit if required.
 Looking for
Top-Tier Residential Proxies?
Looking for
Top-Tier Residential Proxies? 您在寻找顶级高质量的住宅代理吗?
您在寻找顶级高质量的住宅代理吗?
Types of Free Proxy Servers Available in 2026
These are raw directories ofte ...
Jenny Avery
2026-02-01

Web Scraping eCommerce Websites with Python: Step-by-Step
This article provides a detail ...
Yulia Taylor
2026-01-29

10 Best Web Scraping Tools in 2026: Prices and Rankings
In this article, discover the ...
Anna Stankevičiūtė
2026-01-29

Best Bing Search API Alternatives List
Discover the best alternatives ...
Anna Stankevičiūtė
2026-01-27

The Ultimate Guide to Web Scraping Walmart in 2026
Learn how to master web scrapi ...
Jenny Avery
2026-01-24
Concurrency vs. Parallelism: Core Differences
This article explores concurre ...
Anna Stankevičiūtė
2026-01-24

Best Real Estate Web Scraper Tools in 2026
Learn about the leading real e ...
Anna Stankevičiūtė
2026-01-23

Playwright Web Scraping in 2026
Learn how to master Playwright ...
Jenny Avery
2026-01-22

Top 5 Wikipedia Scraper APIs for 2026
In this article, we will help ...
Anna Stankevičiūtė
2026-01-19